Orthopaedics Services
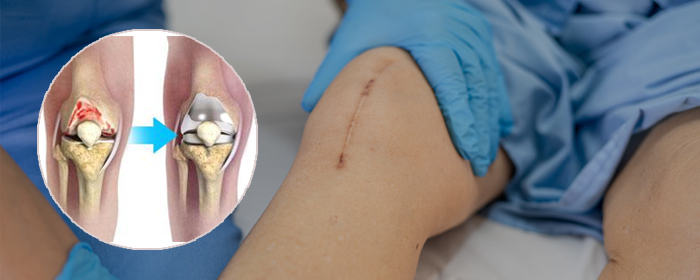
Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) or total knee replacement (TKR) is a common orthopaedic surgery that involves replacing the articular surfaces (femoral condyles and tibial plateau) of the knee joint with smooth metal and highly cross-linked polyethylene plastic. TKA aims to improve the quality of life of individuals with end-stage osteoarthritis by reducing pain and increasing function, and was found to improve patients' sports and physical activity. Knee replacement surgery restores the weight-bearing façade of a damaged, worn, or diseased knee joint. The aim is to remove pain and restore mobility.
Why have knee replacement surgery?
There are three common reasons for the procedure:
- Osteoarthritis: this type of arthritis is age related, caused by the normal wear and tear of the knee joint. It mostly affects patients aged over 50 years, but younger people may have it. Osteoarthritis is caused by inflammation, breakdown, and the gradual and eventual loss of cartilage in the joints. Over time, the cartilage wears down and the bones rub together. To compensate, the bones often grow thicker, but this results in more friction and more pain.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Also called inflammatory arthritis, the membrane around the knee joint to become thick and inflamed. Chronic inflammation damages the cartilage, causing soreness and stiffness..
- Post-traumatic arthritis:This type of arthritis is due to a severe knee injury. When the bones around the knee break or the ligaments tear, this will affect the knee cartilage.
Who might need a knee replacement?
Knee surgery may be suitable for patients who experience:
- Severe knee pain or stiffness that prevents them from carrying out everyday tasks and activities, such as walking, going upstairs, getting in and out of cars, getting up from a chair.
- Moderate but continuous knee pain that continues while sleeping or resting.
- Chronic knee inflammation and swelling that does not improve after taking medications or resting.
- Knee deformity, where there is a noticeable arch on the inside or outside of the knee.
- Depression, resulting from an inability to carry out daily or social activities.
Types of knee replacement surgery
Knee replacement can be total or partial.
- Total knee replacement (TKR): Surgery involves the replacement of both sides of the knee joint. It is the most common procedure. The individual will have less pain and better mobility. Patient is made to walk on 2nd or 3rd day of Surgery. It has excellent results.
- Partial knee replacement (PKR): Partial replacement replaces only one side of the knee joint. PKR is suitable for people with damage to only one part of the knee. Post-operative rehabilitation is more straightforward.